PISTON: Describes a cylindrical plug, closed at one end and open at the other, attached to the connecting rod that slides up and down the cylinder. When the fuel charge is fired, the piston will transfer the explosion's force to the connecting rod and on to the crankshaft.
ALLOY PISTON: Describes a piston produced primarily of aluminium.
DISPLACEMENT: Describes the total volume of air displaced by all the pistons in travelling from the Bottom Dead Centre (BDC) to Top Dead Centre (TDC) positions.
BORE-STROKE RATIO: Describes the relationship between the cylinder bore diameter and the length of the piston's stroke.
DISPLACEMENT VOLUME: Describes a part of the cylinder capacity swept by the pistons on their up and down strokes formed by the bore diameter and the piston stroke.
COLLAPSED PISTON: Describes a piston whose skirt diameter has been reduced due to heat and its forces during the engine's running.
CONNECTING ROD: Describes the connecting link or arm between the piston and the crankshaft that converts the piston's up-and-down (reciprocating) motion into the circular (rotary) motion of the spinning crankshaft.
DEAD SPACE: Describes the space below the piston available for pre-compression of the two-stroke engine's fresh incoming charge.
EXPANDER: Describes the ring placed under a piston ring to increase pressure on the cylinder walls.
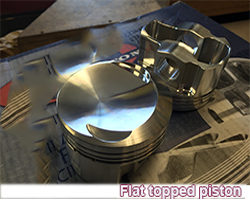
FLAT-TOPPED PISTON: Describes a type of piston that has a flat crown.
FLOATING PISTON PIN: Describes a piston pin free to turn or oscillate in both the connecting rod and the piston.
FORKED CON ROD: Describes a single split connecting rod designed to take two pistons for uniflow-scavenging two-stroke engines.
GAP: Describes the distance between the two ends of piston rings.
GLAZE: Describes an exceptionally smooth, glossy finish found on cylinder walls, caused when piston rings rub up and down the cylinder, "polishing" the cylinder wall and reducing its sealing efficiency.
GROOVED COMPRESSION RING: Describes a scraper-type piston ring.
GUDGEON PIN: Describes a pin used in pistons.
HEAT DAM: Describes a thin groove cut into the head of a piston between the top ring groove and the top of the piston that minimises heat transfer.
L-SECTION RING: Describes a piston ring characterised by its L-shaped cross-section, used primarily on high-performance two-stroke engines.
OIL RING: Describes the lowermost piston ring whose role is to scrape excess oil from the cylinder walls and return it to the oil pan through vents in the ring and piston.
OPERATING PISTON: Describes a piston in an automatic transmission whose role is to cause the respective components to be applied by converting the fluid pressure into mechanical force and movement.
PISTON BORE: Applies to the diameter of the hole in the cylinder block through which the piston moves back and forth between top dead centre (TDC) and bottom dead centre (BDC)
PISTON CHARGING PUMP: Describes a pump whose function is to pre-compress the fresh charge induced into the crankcase in a two-stroke engine.
PISTON CROWN: Describes a crown, situated at the very top of the piston whose role it is to transmit the pressure created during the ignition of the air/fuel mixture through the piston pin, on to the connecting rod, and from there to the crankshaft.
PISTON DISPLACEMENT: Describes the volume of air displaced by a piston when traversing the entire length of its stroke.
PISTON PIN END: Describes the small end of the connecting rod through which the piston pin is inserted
PISTON RING: Describes a metal, split ring installed in the groove on the piston's outside wall that contacts the sides of the ring groove, sealing the space between the piston and the wall. Worn rings can cause low compression and a condition known as blowby, which manifests itself by blue smoke pouring out of the exhaust pipe.
PENT CROWN PISTON: Describes a variation of piston design with a sloping, shaped crown designed to improve the fuel/air mixture's flow, increasing engine compression.
RING GAP: Describes the gap between the piston ring ends with the piston installed in the bore.
SEIZED PISTON: Describes the condition when a piston bonds itself to the sides of the cylinder wall due to a lack of lubricant, causing it to overheat.
STROKE: Details the total distance that the piston moves when travelling between the bottom dead centre (BDC) and top dead centre (TDC).
THRUST BEARING: Describes a bearing fitted with flanges on its two sides whose role is to prevent the crankshaft from moving endwise. If the crankshaft tends to shift one way or another, the crankpin sides come up against the flanges preventing excessive endwise movement.
TOP RING GROOVE INSERT: Describes various piston rings with a nickel-iron metal insert cast into the piston heads, which has the top ring groove cut into it to prolong the useful life of the piston and ring.
All Categories
- Home Page
- Mechanics
Mechanics
Back- Camshaft
- Carburettors A-C
- Carburettors D-F
- Carburettors H-M
- Carburettors R-W
- Clutch B-C
- Clutch D-W
- Cooling System A-C
- Cooling System D-F
- Cooling System H-W
- Crankshaft A-C
- Crankshaft D-W
- Cylinder Head
- Engine A-D
- Engine E
- Engine F-L
- Engine M-S
- Engine T-X
- Filters
- Fuel Control Systems A-E
- Fuel Control Systems F
- Fuel Control Systems M-S
- Gearbox A-D
- Gearbox E-G
- Gearbox H-R
- Gearbox S-W
- Oil Control Systems C-W
- Oil Control Systems
- Pistons
- Auto Electrics
- Brakes,Suspension and Steering
Brakes,Suspension and Steering
Back- Axles
- Brakes A-B
- Brakes E-D
- Brakes FL
- Brakes M-R
- Brakes S-Y
- Differential
- Drive Systems
- Exhaust Systems A-D
- Exhaust Systems E
- Exhaust Systems F-Y
- Hydraulics
- Shock Absorbers
- Springs
- Steering A-R
- Steering S-V
- Suspension A-H
- Suspension I-R
- Suspension S-W
- Tires A-F
- Tires G-B
- Tires S-W
- WheelsA-I
- WheelsI-S
- Wheels T-V
- Bodywork
- Exterior Trim
- Interior Trim
- Paintwork
- Parts and Fittings
- Tools and Equipment
Tools and Equipment
Back 



- Site Map
- Privacy Policy
- Contact Us


All you need to know on how to acquire, restore and maintain a Classic Car
Step back in time to the renaissance age of the UK and European Car Industries
> All that is happening NOW in the world of classic cars.
Step into the golden decade of the UK and European Car Industries
and catch up with all the latest news and features.
Sign up for a Classic Car Info Twitter account.
ae4